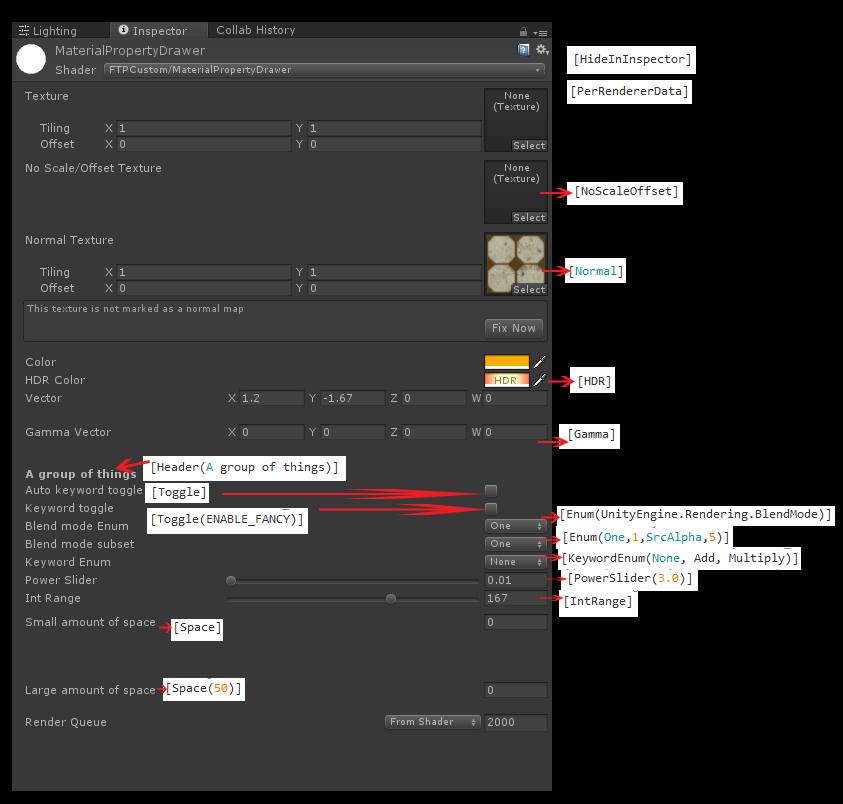
Shader "MaterialPropertyDrawer"
{
Properties
{
_MainTex("Texture", 2D) = "white" {}
[HideInInspector] _MainTex2("Hide Texture", 2D) = "white" {}
Brought to you by Headjack
FFmpeg is one of the most powerful tools for video transcoding and manipulation, but it's fairly complex and confusing to use. That's why I decided to create this cheat sheet which shows some of the most often used commands.
Let's start with some basics:
ffmpegcalls the FFmpeg application in the command line window, could also be the full path to the FFmpeg binary or .exe file
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Shader "Name" { | |
| Properties { | |
| name ("display name", Range (min, max)) = number | |
| name ("display name", Float) = number | |
| name ("display name", Int) = number | |
| name ("display name", Color) = (number,number,number,number) | |
| name ("display name", Vector) = (number,number,number,number) |
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| using UnityEngine; | |
| using System.IO; | |
| using System; | |
| using System.Linq; | |
| using System.Text; | |
| using System.Collections.Generic; | |
| using System.Collections; | |
| public class FFMpegYUV4Texture : MonoBehaviour | |
| { |